AABB's Standards Program has evolved over time in response to advancements in the field. Learn more about AABB's Standards Program below. To request more information about a particular Standard, individuals may request a Standards Clarification.
All sets of AABB Standards are effective for two years. The following are the dates by which all AABB Standards take effect:
| Standard | Effective Date |
| Blood Banks and Transfusion Services | April 1 of even numbered years |
| Cellular Therapy Services | July 1 of odd numbered years |
| Immunohematology Reference Laboratories | April 1 of even numbered years |
| Molecular Testing for Red Cell, Platelet, and Neutrophil Antigens | October 1 of even numbered years |
| Out of Hospital Transfusion Administration Services | TBD |
| Patient Blood Management Program | June 1 of odd numbered years |
| Perioperative Autologous Blood Collection and Administration | January 1 of odd numbered years |
| Relationship Testing Laboratories | January 1 of even numbered years |
AABB Standards represent requirements that must be implemented by AABB-accredited facilities. A requirement contains the word “shall,” which indicates that the statement is mandatory. Failure to meet the requirement would constitute a nonconformance under the AABB Accreditation Program. There are rare instances in which a standard uses the term “may.” A statement that uses “may” is not a requirement.
When the pencil symbol (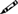 ) precedes a standard, users are required to maintain a record of that activity in order to meet the standard. Users should refer to the reference standard at the end of Chapter 6 to identify the content(s) of the record and the associated retention time.
) precedes a standard, users are required to maintain a record of that activity in order to meet the standard. Users should refer to the reference standard at the end of Chapter 6 to identify the content(s) of the record and the associated retention time.
In the Standards for Cellular Therapy Services, users will note that a (C) or an (F) precedes the pencil symbol. In this case, the (C) and the (F) symbols provide additional details on the required retention time: a (C) indicates that a record must be retained for ten years from the creation of the record, while the (F) symbol indicates that the required retention time is ten years from the final disposition of the product.
In many cases, a requirement in the AABB Standards may be associated with a requirement in the U.S. Code of Federal Regulations (CFR). Unless the standard specifically requires users to follow the requirements in the CFR, the reference is for information only. Under the new electronic publication format, resources such as the CFR can be accessed via a hyperlink in the portal.
Even if the reference to the CFR is informational, users may want to review the FDA requirements, particularly if your facility is subject to FDA regulations. In certain circumstances, the referenced resource may provide additional information, and in some cases, the regulation cited may actually differ from the standard. As a reminder, your facility is responsible for ensuring that all of your policies, processes, and procedures are in compliance with applicable federal, state, and local regulations.
The Standards for Cellular Therapy Services does not comprehensively address all requirements for cellular therapy products also regulated as biological drug products under section 351 of the Public Health Service (PHS) Act. Applicable regulations for these products may include 21 CFR Parts 201, 202, 210, 211, 312, 600, and 610. The CT Standards does not differentiate between 361 or 351 products (as regulated by the PHS Act).
Each edition of AABB's Standards are developed by a team of experts who volunteer their time as a member of a Standards Committee. Each edition of AABB's Standards are based on best medical practice, scientific data, principles associated with good manufacturing practices and quality assurance, and applicable regulations. When possible, the standards are written to be consistent with the requirements of other standards-setting and accrediting bodies and to recognize regulatory environments different from that of the United States.
Much of the ongoing work of AABB's Standards Committees is geared toward helping those in the field understand the process by which standards are set and to understand how to effectively implement the requirements. In an effort to assist users, AABB maintains a Standards Library, which includes Standards-related documents currently available for public review.
Any individual AABB individual member can apply to serve on a Standards Committee. Terms of service last for a minimum of one edition of Standards and a maximum of two editions. Committee membership is determined once every two years for each edition of Standards and approved by the current or incoming chair of the Committee and the AABB Board of Directors.
AABB Standards combine internationally accepted quality management system requirements with relevant technical requirements for each discipline. As such, the Standards can serve as the basis for accreditation anywhere in the world. While some requirements are based on the U.S. FDA’s regulations, a committee with international expertise can review requests for variance that involve a departure from U.S. public health priorities. Learn more about Requesting a Variance.
AABB has also helped international public health systems by using Standards templates to assist the Latin American, Caribbean and African regions in developing region-specific standards. AABB hopes that these Standards templates, which incorporate blood banking terminology and are compatible with the universally accepted ISO (International Organization for Standardization) 9000 standards, can be used as the foundation for standards-setting and accreditation programs in any region of the world.
AABB Releases 35th Edition of BB/TS Standards
March 02, 2026
AABB Releases 14th Edition of IRL Standards
February 23, 2026
AABB Outlines Notable Changes to Upcoming BB/TS Standards, IRL Standards
February 11, 2026